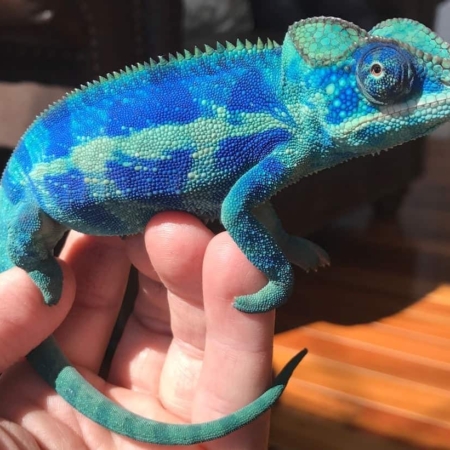
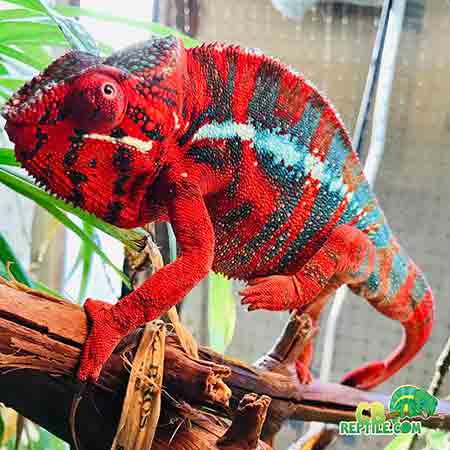
Male Panther Chameleon Display, Courtship & Breeding Behavior
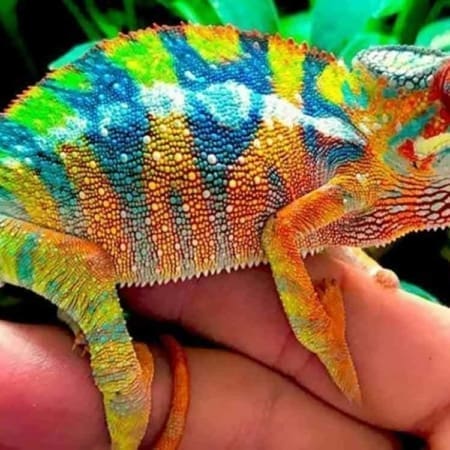
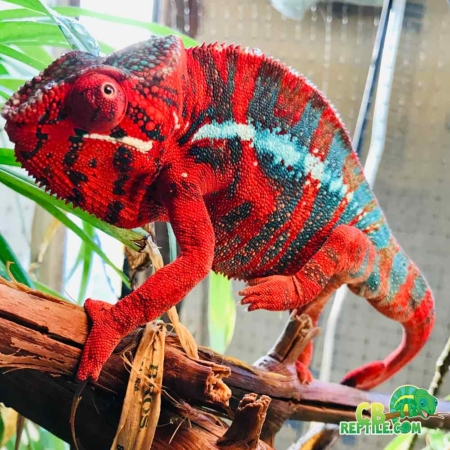
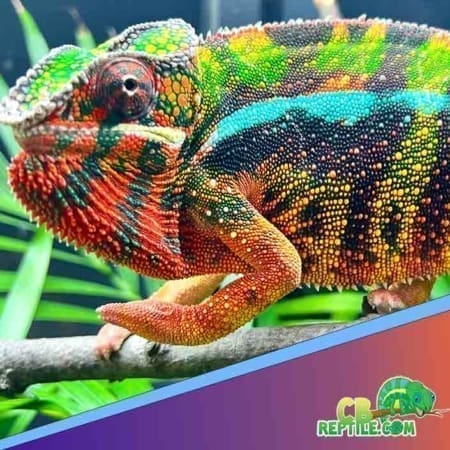
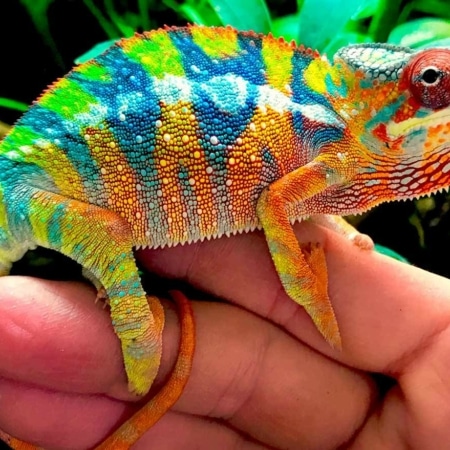
Male panther chameleons are among the most visually impressive reptiles in the world, known for their vibrant coloration, dramatic displays, and complex courtship behavior. During breeding season, males use a combination of color shifts, body posture, locomotion patterns, and subtle behavioral cues to communicate with females and deter rival males. Understanding these behaviors is essential for responsible breeding, stress-free introductions, and maintaining the long-term health of both partners.
Because behavior is heavily influenced by genetics and early husbandry, beginning with a captive-bred male from the best panther chameleon breeders ensures stable temperament, strong coloration, and predictable breeding behavior. Captive-bred males are easier to read, healthier, and produce more consistent offspring.
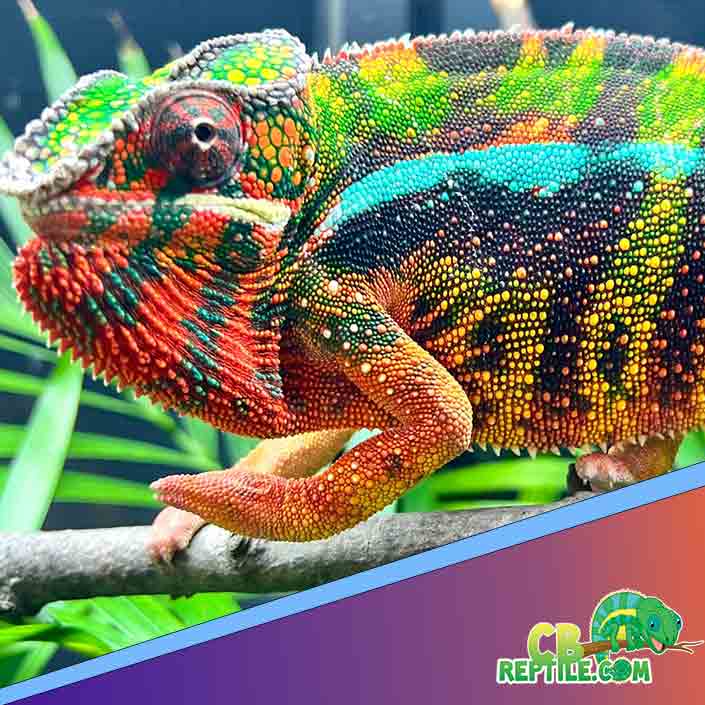

The Biology Behind Male Display Behavior
Male panther chameleons use visual displays for three purposes:
- Attracting receptive females
- Warning off competing males
- Establishing dominance within a territory
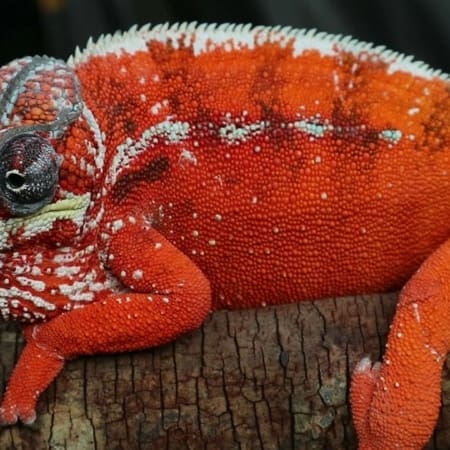
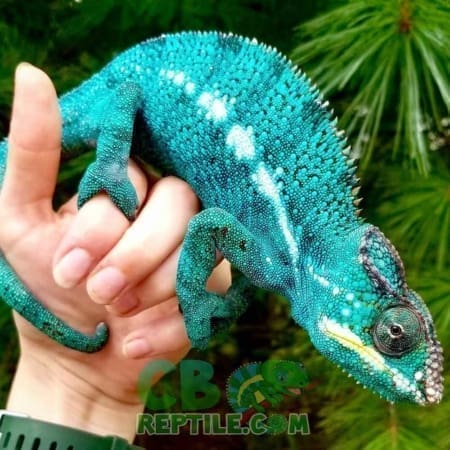
Color is the primary method of communication. Males intensify specific pigments when excited, territorial, or courting. Each locale displays distinct colors—Ambilobe males may flash neons, reds, and blues, while Nosy Be males display electric blue and teal.
Baseline Male Behavior Outside Breeding Season
Outside breeding windows, males remain calm, display baseline coloration, and behave predictably. They may:
- Maintain moderate but vibrant coloration
- Move confidently throughout the enclosure
- Display interest in food and hydration
- Show mild territorial behavior when approached
These baseline behaviors help breeders recognize when behavior changes toward reproductive signals.
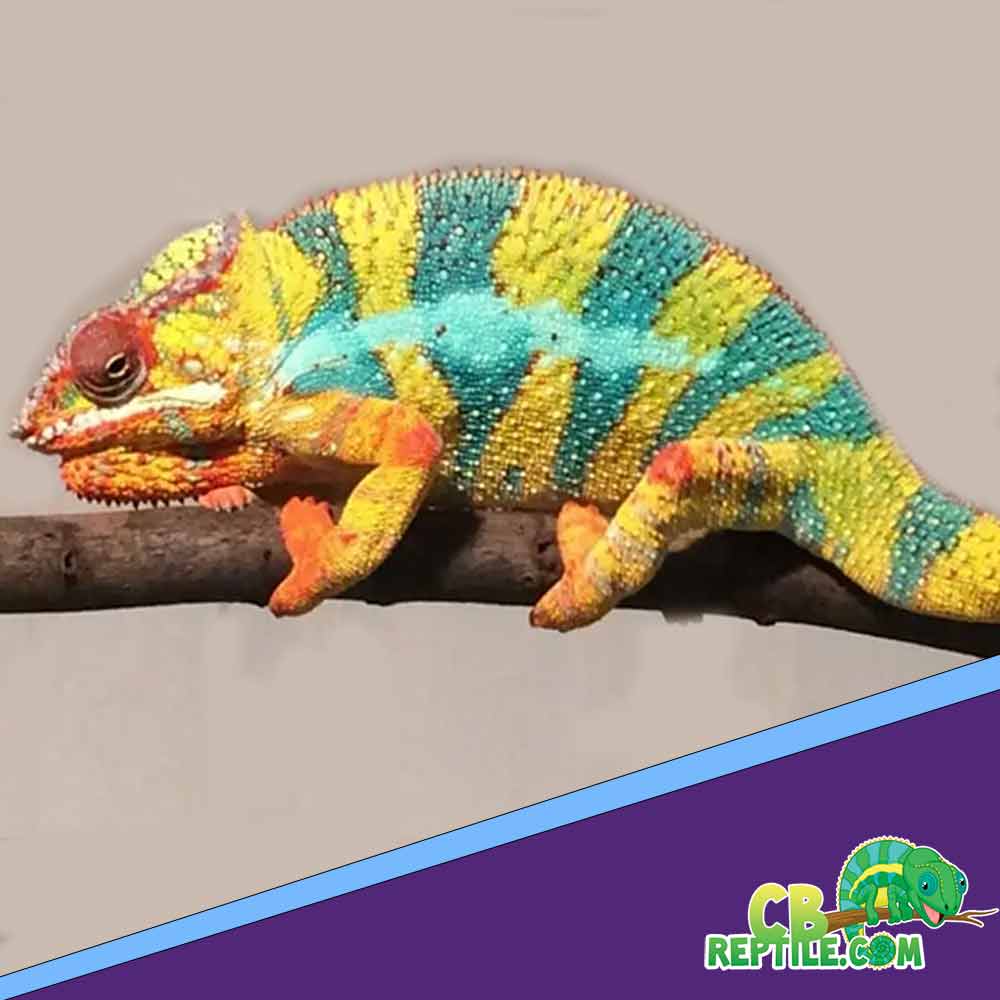

Signs a Male Panther Chameleon Is Ready to Breed
Before introducing a male to a female, the male must be physiologically and behaviorally ready. Typically, males reach sexual maturity around 10–12 months of age.
Signs of male breeding readiness:
- Increased coloration intensity
- More frequent basking
- Heightened awareness of surroundings
- Displaying more often when seeing movement
- Slow, deliberate body rock when stimulated
A fully mature male is confident, visually vivid, and behaviorally assertive.
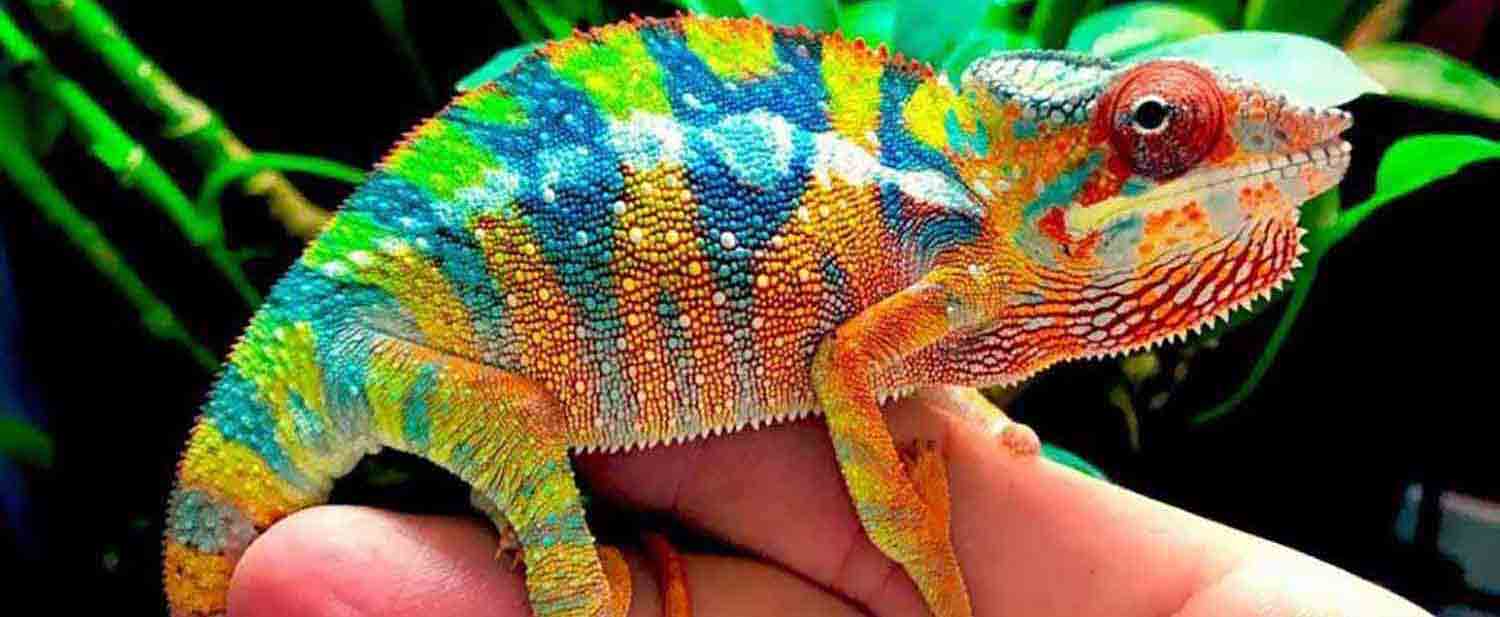
Male Courtship Displays
When a male sees a receptive female, his behavior shifts dramatically into courtship mode. Unlike aggression, courtship is smoother, slower, and often accompanied by increased color brightness.
Key courtship displays include:
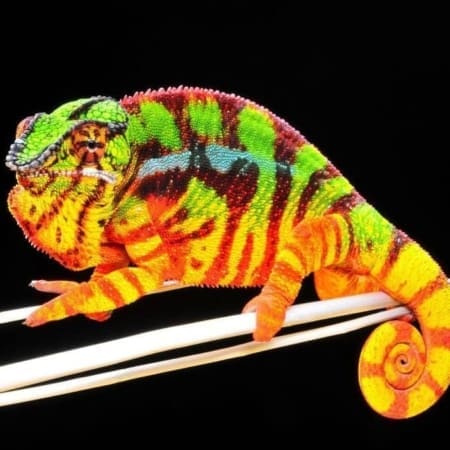
1. Color Intensification
Males may brighten dramatically—reds deepen, blues intensify, yellows become neon-like, and the entire body shifts into a bold display palette.
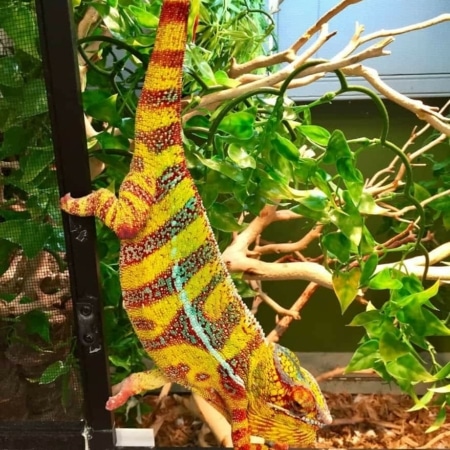
2. Lateral Flattening
The male expands his body sideways to appear larger, making his colors more visible.
3. Courtship Rocking
Distinct slow rocking motions signal interest. This motion is not aggressive but rhythmic.
4. Approaching the Female Slowly
A receptive female will tolerate this approach, while a non-receptive one will reject it.

Distinguishing Courtship from Aggression
Male displays sometimes resemble territorial aggression, so it’s essential to know the differences.
Signs of Courtship:
- Slow, controlled rocking movements
- Bright, clean coloration
- Calm approach toward female
- No gaping or hissing
Signs of Aggression:
- Dark bars or mottled coloration
- Rapid body flattening
- Gaping or hissing
- Charging or sudden lunging
Never allow aggressive interaction; separate immediately.
Territorial Behavior Toward Other Males
Males are highly territorial in nature. Even visual contact with another male can trigger stress or display responses.
Signs of male-to-male territorial behavior:
- Color flashing
- Gaping aggressively
- Extended body posture
- Branch-gripping and tail curling
For this reason, breeding rooms must ensure males cannot see each other.
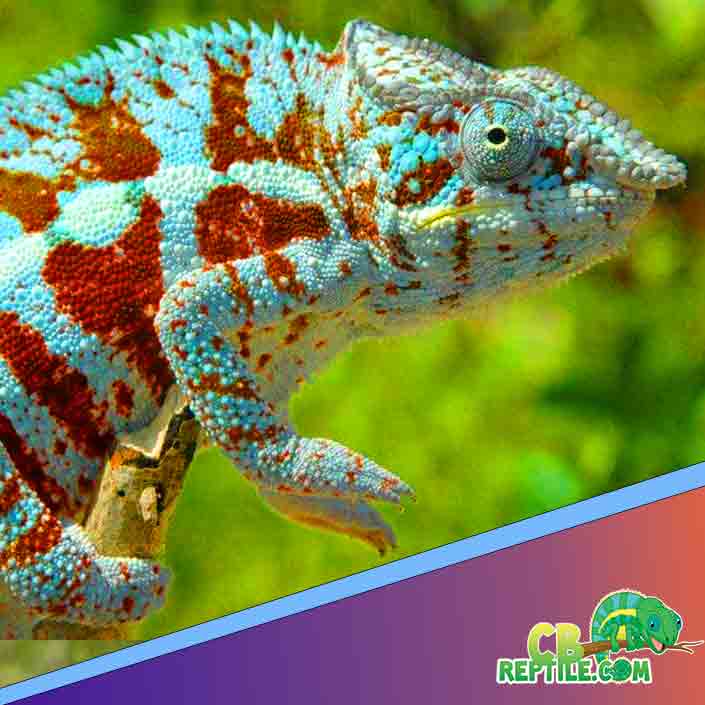

Male Response to Receptive Females
A receptive female triggers immediate visual and behavioral shifts in the male.
Typical male responses:
- Approaching with confidence
- Displaying full flank colors
- Following the female’s movement
- Attempting to mount if allowed
These behaviors confirm sexual readiness.
The Breeding Interaction
1. Introduction
Place the receptive female into the male’s enclosure, not the other way around.
2. Observation
Watch closely for acceptance or refusal. A receptive female remains calm; a non-receptive female rejects him.
3. Mounting
If accepted, the male mounts gently and positions himself to align with the female.
4. Copulation
The mating process can last from 5 minutes to over 45 minutes.
5. Separation
Separate immediately after successful copulation to prevent post-breeding aggression.
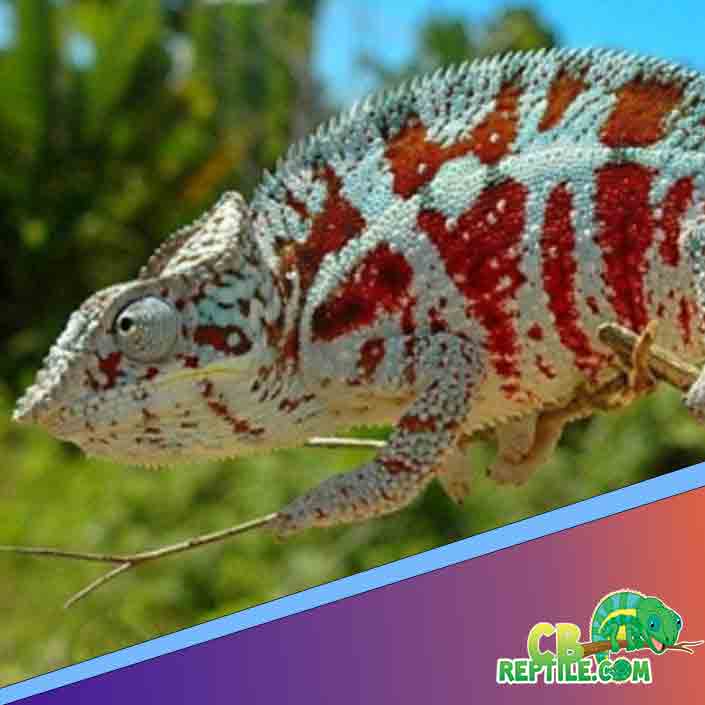

After Breeding: Male Behavioral Reset
After copulation, males may temporarily elevate their basking time or display heightened alertness. Within 24–48 hours, behavior typically returns to baseline.
Common temporary changes:
- Slight increase in color intensity
- Mild territorial displays
- Increased food interest
Males generally recover quickly and are ready for breeding again within a few weeks, depending on age and condition.
Optimizing Male Health for Breeding
Healthy males produce better offspring and display stronger, more consistent breeding behavior.
Male conditioning includes:
- High-quality feeders (silkworms, roaches, BSFL)
- Strong UVB exposure
- Appropriate hydration cycles
- Calcium supplementation (without D3 3–4x weekly, with D3 every 2 weeks)
- Minimal handling during breeding season
Strong conditioning equals strong performance in pairing.
Choosing the Best Male for Breeding Programs
When browsing a chameleon for sale near me, selecting a vibrant, healthy, captive-bred male with predictable lineage ensures successful pairing results. A reputable breeder ensures you know the best places to purchase panther chameleon with strong genetics, stable temperament, and high breeding potential.
Final Thoughts on Male Courtship Behavior
Male panther chameleons exhibit some of the most fascinating display behaviors in the reptile world. By understanding their color signals, posture, courtship rituals, and territorial triggers, breeders can safely facilitate successful pairings while minimizing stress. A well-prepared male, paired with a receptive female under controlled conditions, produces predictable behavior and excellent breeding outcomes.